Strengthening the Home Based Newborn Care (HBNC) System — UNICEF Ranchi (2018)
Strengthening the Home Based Newborn Care (HBNC) System — UNICEF Ranchi (2018)
The Challenge
Jharkhand, one of India’s most health-challenged states, faces persistently high neonatal mortality rates driven by inadequate postnatal care, limited health worker capacity, and fragmented data systems. The Home Based Newborn Care (HBNC) programme, a critical Government of India initiative, deploys community health workers known as Sahiyas (ASHAs) to conduct home visits for newborns and their mothers during the critical first 42 days of life. These visits cover essential newborn care practices including thermal care, breastfeeding support, infection prevention, and danger sign identification.
UNICEF Ranchi, supporting the Government of Jharkhand’s health department, identified serious systemic challenges in the HBNC programme:
- Paper-Based Data Collection: Sahiyas across Jharkhand’s districts were recording HBNC visit data on paper forms, leading to significant delays in data compilation, frequent data entry errors, and near-impossible real-time monitoring of home visit completion rates.
- No Real-Time Monitoring: Programme managers at block, district, and state levels had no mechanism to track whether Sahiyas were completing their mandated home visits, leaving newborns potentially without critical care during the vulnerable neonatal period.
- Weak Reporting Systems: The absence of a digital reporting system meant that HBNC performance data took weeks or months to be aggregated, analyzed, and acted upon — by which point intervention opportunities had been lost.
- Training and Capacity Gaps: Identifying which Sahiyas needed additional training or support required manual review of paper records, making it nearly impossible to target capacity-building efforts effectively.
- Accountability Challenges: Without digital tracking, there was no reliable mechanism to verify visit completion, identify coverage gaps, or hold the system accountable for ensuring every newborn received mandated care.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: State and district health officials lacked the analytical tools and dashboards needed to make evidence-based decisions about resource allocation, intervention targeting, and programme improvement.
Velocity’s Solution
Scope of Work
Velocity Software Solutions designed and developed a comprehensive digital system to strengthen the HBNC programme in Jharkhand, encompassing a web-based monitoring platform, mobile application for field-level data collection, and business analytics dashboards for programme management.
Key Features & Deliverables
1. Web-Based HBNC Monitoring Portal
- Centralized web portal for real-time monitoring of HBNC visit data across all districts, blocks, and sub-centres in Jharkhand
- Role-based access control for State, District, Block, and Sub-Centre level users
- Data entry interfaces for digitizing HBNC home visit records
- Comprehensive data validation rules to minimize errors and ensure data quality
- Integration with existing health information systems
- Secure data storage with backup and recovery mechanisms
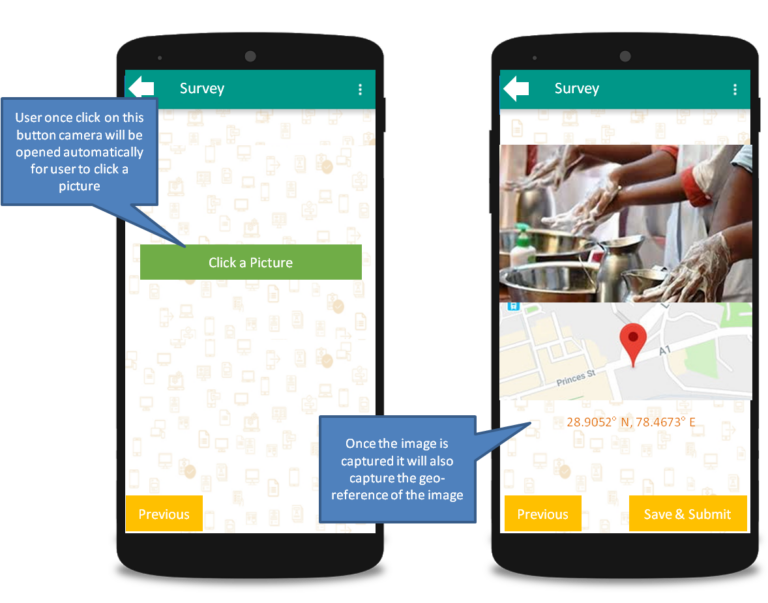
2. Mobile Application for Field Data Collection
- Android-based mobile application for Sahiyas and field supervisors
- Offline-capable data entry forms mirroring HBNC visit checklists
- Automatic data synchronization when connectivity is available
- GPS-enabled visit verification to validate home visit locations
- Push notification system for visit reminders and alerts
- Simplified user interface designed for community health workers with varying levels of digital literacy
3. Business Analytics and Dashboards
- Interactive dashboards at state, district, block, and sub-centre levels
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) including:
- Home visit completion rates by geography and time period
- Newborn coverage percentages
- Danger sign identification and referral rates
- Sahiya performance metrics
- Trend analysis and comparison across districts
- Drill-down capability from state-level summaries to individual Sahiya performance
- Exportable reports in multiple formats (Excel, PDF) for programme reviews
- Anomaly detection highlighting areas with unusually low visit rates or data quality concerns
4. Sahiya Management Module
- Complete registry of all Sahiyas with their assigned areas and contact information
- Performance tracking and scoring based on visit completion and data quality
- Training needs identification based on performance analytics
- Automated alerts for supervisors when visit completion rates fall below thresholds
5. Reporting and Analytics
- Automated generation of periodic reports (weekly, monthly, quarterly)
- Custom report builder for ad-hoc analysis
- Data export capabilities for integration with state and national reporting systems
- Graphical dashboards with maps, charts, and infographics for stakeholder presentations
Technology Stack
- Web Platform: PHP-based web application with responsive design
- Mobile Application: Android native application with offline capability
- Database: MySQL with optimized query performance for large datasets
- Dashboard: Interactive business analytics with charting libraries
- Hosting: Secure server hosting with SSL encryption
- Integration: API-based integration with health information systems
- Notifications: SMS and push notification services
Implementation Approach
- Requirements Gathering: Conducted field visits and stakeholder consultations across multiple districts in Jharkhand to understand HBNC workflows, Sahiya work patterns, supervisory structures, and data needs at each level.
- System Design: Developed comprehensive system architecture, user interface wireframes, and database schemas aligned with HBNC programme requirements and UNICEF’s technical standards.
- Iterative Development: Built the web portal, mobile application, and dashboard components in iterative cycles with regular demonstrations to UNICEF and government health officials.
- Field Testing: Conducted pilot testing in selected blocks with actual Sahiyas and supervisors, gathering feedback on usability, performance, and workflow alignment.
- Training and Rollout: Delivered training sessions for users at all levels — from Sahiyas using the mobile app to state-level officials using the dashboards — with hands-on practice and reference materials.
- Deployment of Resources: Deployed dedicated technical resources at the Ranchi office to provide on-ground support, handle customization requests, and ensure smooth system adoption.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitored system usage, performance, and data quality, making iterative improvements based on user feedback and programme needs.
Key Outcomes & Impact
- Digital Transformation of HBNC Monitoring: Transitioned the HBNC programme from a paper-based system to a real-time digital monitoring platform, enabling timely interventions for newborn care across Jharkhand.
- Improved Newborn Coverage: Real-time visibility into home visit completion rates enabled programme managers to identify and address coverage gaps quickly, ensuring more newborns received mandated care during the critical neonatal period.
- Data-Driven Programme Management: State and district health officials gained access to comprehensive dashboards and analytics, enabling evidence-based decisions about resource allocation, training priorities, and programme strategy.
- Enhanced Accountability: Digital tracking of Sahiya visits with GPS verification created a transparent accountability framework, motivating consistent home visit completion and enabling performance-based supervision.
- Reduced Reporting Delays: Automated report generation eliminated weeks of manual data compilation, providing programme leadership with near-real-time performance data for timely decision making.
- Capacity Building Intelligence: Performance analytics identified specific knowledge and skill gaps among Sahiyas, enabling targeted training interventions that improved the quality of newborn care delivered during home visits.
- Scalable Model: The system architecture was designed for scalability, creating a model that could be replicated across other states implementing the HBNC programme.
Why Velocity?
Velocity Software Solutions was selected through UNICEF’s competitive procurement process based on its proven expertise in building health programme monitoring systems and mobile data collection platforms for development organizations. Velocity’s deep understanding of India’s community health worker ecosystem, its experience with field-level data collection challenges (connectivity, device constraints, user literacy), and its track record of delivering UNICEF projects made it the ideal partner. The team’s ability to deploy dedicated resources at the Ranchi field office ensured hands-on support during the critical adoption phase, while its analytics capabilities provided the programme management tools that health officials needed to improve newborn care outcomes.
Velocity Software Solutions — Harnessing technology to strengthen community health systems and save newborn lives.